Interacting without touching technology
The future is contactless!
We trigger many actions by touching a button on technical devices. By touching a switch, we tell it to turn on the light, start a machine, or call the elevator to the desired floor. But through technological progress, we have harnessed a new way to operate switches: contactless control
Don’t touch it!
Contactless control traces its beginnings back to the process of automation. A typical example of this is automatic lighting control or door opening which reacts to movements. This simple form of contactless control is a matter of course for us. It is relatively new development that there are now alternatives to conventional switch systems available on the market.
Manufacturers are welcoming this new trend, and demand is high. The underlying causes vary. With some applications, physical contact with user interfaces may prove detrimental, for example, when the components are very sensitive. Or the environment might designed in such a way that it is impossible to have any direct contact.
In yet other cases, people might avoid contact, for example, if the surface comes in contact with numerous people. Contactless interaction boasts significant benefits.
There are three reasons why more and more equipment manufacturers are opting for a contactless control:
Technological approaches to choose from.
Non-contact control can be implemented using various technologies, and the choice is usually between infrared, ultrasound, laser, or radar. The basic principle is similar: a transmitting antenna emits a signal that changes or is interrupted when it hits an object. This change or reflection is analysed by the system and yields information. For example, the technology detects the movement of an object from a distance.
Depending on the requirements and specifications of the application, the one or the other technology may be better- or worse-suited. The following table shows a performance comparison of the widely used sensor technologies based on evaluation criteria relevant to the given application.
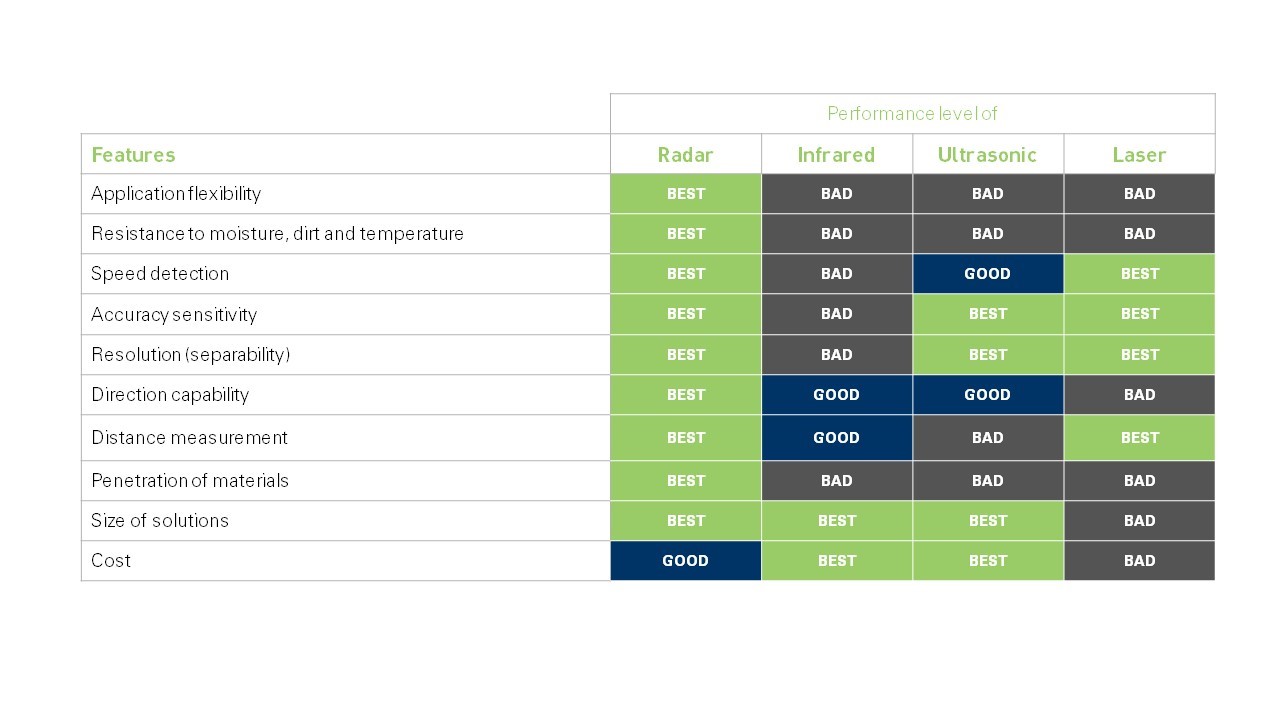
picture: ©InnoSenT GmbH
In addition to the aforementioned sensors, even cameras are in use. Here, the system recognises movement through changes to pixels and complex algorithms. However, this approach is very expensive and elaborate.
Two variants of contactless control.
Current contactless control systems can be broken down into two types according to their operating principle. With the one variant, the sensor and person interact completely without them noticing – passively. And with active control, a person triggers a specific action.
The type of application that is suitable for your application depends on the task that the sensor system is meant to perform. The intended use and environment also play a role in selection. Because the two contactless control types differ in their functionality and therefore take on different application tasks.
These articles describe the two variants in more detail:
A special form of contactless operation is voice control. While technology is advancing swiftly and performance is improving, this comes at a great cost: data protection advocates view systems’ permanent operation readiness and possibility of listening in as a problem.
Radar impresses.
The demand for radar sensors in the smart home and building automation sector is booming. This can be attributed to the following five advantages, amongst others:
- anonymous detection
- insensitivity to weather and temperature
- no dependence on light
- precise measurement accuracy
- placement behind plastics and other materials possible
In addition, further technical developments are also making radar increasingly attractive. The products are now available at low prices and boast greater functionality than PIR sensors.
The detection principle works with electromagnetic waves, similarly to the echolocation of bats. This way, radar records extensive information about the events and objects within its detection range. This helps to make detection more accurate and reliable. In addition, radar-based systems are very robust and ideally equipped for indoor and outdoor use. Radar makes our day-to-day lives smart, convenient, & safe.
Successfully deployed
Radar sensors already impress through their many applications. From the kitchen to the bathroom – we encounter the technology in every room. Modern refrigerators respond to a person in front of it or entering the room. Instead of using a touch display, the coffee machine detects a person’s presence or movement in front of the control panel. Building doors, garage doors, windows, or cabinets are opened using proximity switches. Even the toilets are now available equipped with motion sensors. All household appliances or lamps can theoretically be controlled without skin contact.
The radar experts at InnoSenT GmbH have been developing various 24 GHz sensor solutions for this purpose which precisely meet the market requirements and those of the industry for many years. On the company homepage you will discover which products are suitable for this application area and find out more information about their features.
Header Picture Source: © slavun by adobe stock
Share this Content
Building Automation & Smart Home
Contactless and intelligent control for modern technology
Radar sensors take on many tasks for us, thus making our everyday lives easier, safer, and more efficient. They are a kind of sensory organ for objects for perceiving their surroundings. These technological assistants open up new possibilities for operating devices: contactless interaction between humans and devices. The sensors are the link for triggering or automating certain actions without contact or automating them.